Report on IFRS 17 Implementation in Asia: Comparisons and Impacts
- EverBright Actuarial
- Aug 3, 2025
- 5 min read
Updated: Aug 19, 2025
International Financial Reporting Standard 17 (IFRS 17), issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), represents a major overhaul in accounting for insurance contracts.

Effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2023, it aims to enhance transparency, comparability, and consistency in insurers' financial statements by introducing principles-based measurement models, including the Contractual Service Margin (CSM), risk adjustment, and discounting of cash flows.
As of August 2025, implementation varies globally, with significant implications for the insurance industry. This report focuses on IFRS 17 adoption in Asia, compares it to other regions, examines country-specific statuses within Asia, and analyzes impacts on various lines of business and insurer types. Data is organized into tables for clarity.

IFRS 17 Implementation Status in Asia
Asia exhibits a mixed adoption landscape for IFRS 17, with many jurisdictions aligning with the 2023 effective date, while major economies like China and India have deferred implementation to 2025 or 2026 due to complexity and local regulatory adjustments. Smaller markets face challenges in resources and technical expertise, leading to ongoing struggles even post-adoption. The following table summarizes the status for key Asian countries based on available data as of 2025.
Country | Adoption Status | Effective Date | Notes/Defferals/Modifications |
China | Deferred | January 1, 2026 | Delayed for alignment with local standards; ongoing progress in mainland and Hong Kong. |
India | Deferred | 2026 | Postponed to allow for industry preparation; not fully adopting IFRS framework. |
Japan | Not Adopting | N/A | Relies on local GAAP; some multinational insurers apply IFRS internally. |
Indonesia | Not Adopting | N/A | Uses local standards; no plans for IFRS 17. |
Philippines | Deferred | January 1, 2027 | Optional early adoption allowed; insurers may adjust reports earlier. |
Hong Kong | Adopted | January 1, 2023 | Full implementation; challenges in actuarial modeling for life products. |
South Korea | Adopted | January 1, 2023 | Integrated with local regulations; focus on life insurance impacts. |
Singapore | Adopted | January 1, 2023 | Smooth transition; enhanced transparency for regional insurers. |
Malaysia | Adopted (Converged) | January 1, 2023 | Full convergence announced; applicable to listed insurers. |
Taiwan | Adopted | January 1, 2023 | Parallel to ICS adoption in 2026; focus on P&C sectors. |
Thailand | Deferred | January 1, 2025 | Parallel runs in 2024; industry-wide preparation ongoing. |
Vietnam | Planned | 2025 | Strategic plan for full IFRS adoption, including IFRS 17. |
This table highlights variability: advanced economies like Singapore and Hong Kong adopted promptly, while populous markets deferred, impacting regional comparability.

Comparison with Other Regions
Globally, IFRS 17 adoption is widespread in over 140 jurisdictions, but exceptions in major economies (e.g., US, China) limit uniformity. Europe leads with near-universal adoption, enhancing cross-border comparability.
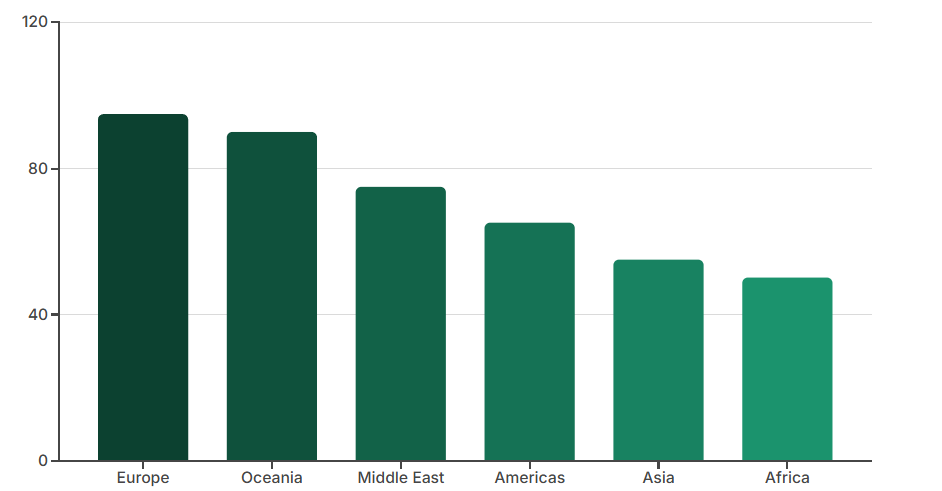
The Americas show divergence, with Canada adopting but the US sticking to GAAP. Africa and the Middle East have partial adoption, often in financial hubs, while Oceania aligns closely with IFRS. Asia lags due to deferrals in large markets, leading to fragmented reporting compared to Europe's standardized approach. Qualitatively, Asia's adoption rate is around 50-60% for key insurers as of 2025, versus 90%+ in Europe.
The table below provides a regional overview:
Region | Adoption Level (as of 2025) | Key Examples | Comparison to Asia |
Europe | High (Nearly 100%) | EU/EEA countries adopted 2023; UK post-Brexit alignment. | More uniform and earlier adoption; better comparability than Asia's mixed status. |
Americas | Medium (Varies) | Canada adopted 2023; US/GAAP no; Brazil yes. | Similar to Asia in divergence, but fewer deferrals; Asia has more large-market holdouts. |
Africa | Low-Medium | South Africa adopted 2023; others partial or local. | Comparable to Asia's variability, but lower overall adoption; Asia benefits from APAC economic ties. |
Middle East | Medium-High | UAE, Saudi Arabia adopted 2023; convergence in GCC. | Higher than Asia in financial centers; Asia's deferrals create more volatility. |
Oceania | High | Australia, New Zealand adopted 2023 (NZ full capture 2025). | Similar to Europe; faster and more complete than Asia. |
Asia's slower pace in major countries contrasts with Europe's efficiency, potentially affecting investor confidence and cross-regional M&A.
Analysis of Impacts on Different Lines of Business
IFRS 17 introduces standardized measurement, but impacts vary by contract duration and risk profile. Life insurance faces the most disruption due to long-term contracts and CSM mechanics, while non-life lines see moderate changes from discounting. Overall, it boosts transparency but increases volatility in earnings.
Line of Business | Key Changes under IFRS 17 | Impact Level | Effects on Businesses |
Life Insurance | CSM for unearned profit; discounting; OCI for changes. | High | Greater volatility in P&L; better visibility of long-term profitability; major impact on annuities and savings products. |
Non-Life/General | Discounting of cash flows; risk adjustment for claims. | Medium | Less disruption than life; improved reserving accuracy; smaller earnings shifts. |
Property | Fulfilment cash flows; no interim reporting exemptions. | Medium | Enhanced comparability; discounting affects short-tail claims minimally. |
Casualty | Risk adjustment; aggregation at portfolio level. | Medium-High | Higher for long-tail lines (e.g., liability); increased transparency but actuarial complexity. |
Life lines experience structural growth visibility, while property/casualty focus on operational efficiency.
Analysis of Impacts on Different Types of Insurers
Impacts differ by insurer size, focus, and operations. Large and life-focused insurers face higher costs but gain from comparability, while small and general insurers struggle with implementation burdens. Reinsurers deal with added volatility.
Type of Insurer | Key Impacts | Challenges | Opportunities |
Large Insurers | Complex portfolio remeasurement; higher compliance costs. | Resource-intensive transitions; multinational reconciliations. | Improved investor appeal; better risk management. |
Small Insurers | Proportional allocation challenges; tech upgrades. | High relative costs; expertise gaps. | Simplified reporting if contracts are short-term. |
Life Insurers | CSM and discounting volatility. | Earnings fluctuations; actuarial modeling. | Transparent profitability for long-term contracts. |
General (P&C) Insurers | Introduction of discounting for non-life. | Moderate changes; focus on claims reserving. | Enhanced comparability with minimal disruption. |
Reinsurers | Economic valuation; loss recovery components. | Volatility from remote risks; reinsurance mismatches. | Better capital allocation; funding avenues. |
Large life insurers and reinsurers see the most transformation, while small general insurers prioritize cost control.

Conclusion
IFRS 17's implementation in Asia is progressing unevenly, with deferrals in key markets hindering regional harmony compared to Europe's robust adoption. Impacts are profound for life and long-tail businesses, driving transparency but demanding adaptations. As adoption matures by 2027, Asian insurers could achieve global parity, benefiting stakeholders through improved financial insights. Ongoing monitoring of deferrals and impacts is recommended.
For insurers navigating the complexities of IFRS 17 adoption in Asia, EverBright Actuarial Consulting offers specialized expertise to ensure seamless compliance and strategic advantage. Founded in 2014 and based in Hong Kong, EverBright provides comprehensive actuarial services, including pricing, risk management, appointed actuary support, and tailored solutions for life, health, group medical, and digital insurance sectors. With a proven track record in delivering innovative insights, our team helps clients mitigate volatility, enhance transparency, and optimize financial reporting under IFRS 17. Visit www.ebactuary.com to explore how EverBright can support your IFRS journey and drive sustainable growth in the evolving insurance landscape.



Comments